Abstract
Introduction
Del(17p) detected by fluorescence in situ hybridisation (FISH) of bone marrow plasma cells (BMPCs) is an adverse prognostic factor in patients with multiple myeloma (MM). While the natural history and prognostic factors in patients with del (17p) detected at diagnosis have been studied, the outcomes of patients who acquire del (17p) later in their course are not known. We aimed to define the outcomes of MM patients who acquire del(17p).
Methods
We reviewed the Dysproteinemia database at Mayo Clinic, MN to identify 80 patients with MM who had their first FISH test negative for del (17p), but acquired del(17p) later in the course of the disease. Sixty (75%) patients had their first FISH within 6 months (mo) of diagnosis; 20 (25%) patients had their first FISH more than 6 mo after diagnosis of MM. Del(17p) included del(17p13.1) and/or monosomy 17. We identified 2 control patients for each case, who were diagnosed during the same time period, but did not demonstrate del (17p) at any time during follow-up.
Results
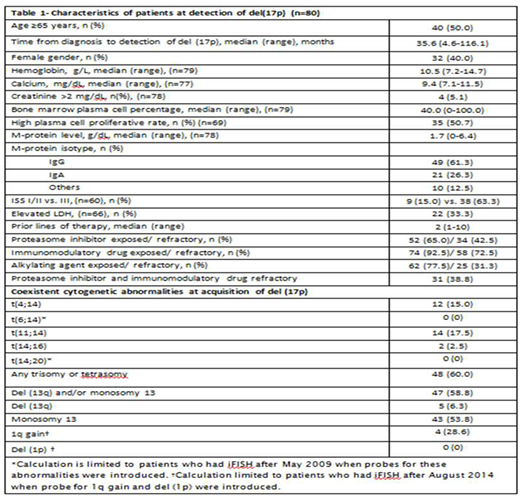
Characteristics of patients at acquisition of del(17p) are shown in Table 1. Of these, 76 patients had relapsed and/or refractory MM; in 4 patients, del (17p) was detected after having attained a response to prior therapy. Seventy (87.5%) patients had del (17p13.1); 5 (6.3%) patients had monosomy 17; 1 (1.2%) patient had both del (17p13.1) and monosomy 17. Four (5.0%) patients had relative loss of 17p. High-risk translocations (HRT) [t(4;14), t(14;16) and t(14;20)] were present in 14 (17.5%) patients. The percentage of PCs with del(17p) were available in 75 patients. The median percentage of PCs with del(17p) was 76 (range, 9-100).
Sixty two (77.5%) patients received exclusively chemotherapy as subsequent treatment; stem cell transplant (SCT) was part of the next treatment in 16 (20%) patients (allogeneic SCT in 1). Among 71 evaluable patients, ≥very good partial response and ≥partial response were attained in 24 (33.8%) and 35 (49.2%) patients respectively. The median progression free survival (PFS) from detection of del (17p) was 5.7 mo (95% CI, 3.5-7.8); overall survival (OS) was 18.2 mo (CI, 13.1-27.5). From a comparable time point, the OS for 160 controls was 56.2 mo (CI, 37.1-75.3) (P<0.001). The results were similar when patients were stratified based on variables at diagnosis such as age, presence of HRT, international staging system (ISS) stage, serum lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) and PC proliferative rate, and proteasome inhibitor (PI)-containing induction and SCT within a year of diagnosis and before acquisition of del(17p). Evaluating outcomes from initial diagnosis, PFS in the acquired del (17p) and control groups were 23.0 (CI, 20.2-25.8) and 30.2 (CI, 26.7-33.9) mo (P=0.028) and OS were 68.2 (CI, 50.8-74.8) and 111.6 (CI, 103.4-127.8) mo respectively (P<0.001). High LDH at baseline [OR- 4.31 (CI, 1.34-13.86)] predicted acquisition of del(17p) while presence of HRT showed borderline significance [OR- 2.02 (0.90-4.54)]. Age ≥65 yrs, ISS III vs. I/II stage, t(11;14), any trisomy, monosomy 13, BMPC%, initial therapy and SCT in first year and before acquiring del (17p) were not predictive.
We performed univariable analysis with variables at detection of del(17p) such as age ≥65 vs. <65 years, serum creatinine >2 vs. ≤2 mg/dL, BMPC% ≥50 vs. <50%, ISS III vs. I/II stage, elevated vs. normal LDH, presence vs. absence of a HRT, presence vs. absence of monosomy 13, presence vs. absence of any trisomy, high vs. low PC proliferation rate, PI and immunomodulatory drug (IMiD)-refractoriness and percentage of PCs with del(17p) as independent variables to determine their association with PFS and OS. ISS stage III, high PC proliferative rate and PI and IMiD-refractoriness were selected after univariable analysis and included in the multivariable Cox proportional hazards model. A higher PC proliferative rate alone predicted shorter OS. None of the above factors were associated with shorter PFS. The median OS in those with high PC-proliferative rate from detection of del(17p) was 10.9 mo (CI, 6.0-17.1) vs. 37.2 mo (CI, 18.2-47.5) in those with low PC proliferative rate (P=0.005).
Conclusion
The prognosis of patients who acquire del (17p) is poor with OS of 6.5 years against 9 years from diagnosis in patients who do not acquire del (17p). This was valid across prognostic sub-groups. High PC proliferative rate was the only factor which impacted OS once patients acquired del(17p).
Kapoor:Celgene: Research Funding; Takeda: Research Funding. Gertz:Research to Practice: Consultancy; Teva: Consultancy; Ionis: Honoraria; annexon: Consultancy; Physicians Education Resource: Consultancy; Abbvie: Consultancy; spectrum: Consultancy, Honoraria; Prothena: Honoraria; Alnylam: Honoraria; Apellis: Consultancy; Medscape: Consultancy; Amgen: Consultancy; janssen: Consultancy; celgene: Consultancy. Lacy:Celgene: Research Funding. Dingli:Alexion Pharmaceuticals, Inc.: Other: Participates in the International PNH Registry (for Mayo Clinic, Rochester) for Alexion Pharmaceuticals, Inc.; Alexion Pharmaceuticals, Inc.: Other: Participates in the International PNH Registry (for Mayo Clinic, Rochester) for Alexion Pharmaceuticals, Inc.; Millennium Takeda: Research Funding; Millennium Takeda: Research Funding. Dispenzieri:Celgene, Takeda, Prothena, Jannsen, Pfizer, Alnylam, GSK: Research Funding. Russell:Vyriad: Equity Ownership. Kumar:AbbVie: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Roche: Research Funding; Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Merck: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Janssen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Oncopeptides: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; KITE: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Janssen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Takeda: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; AbbVie: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; KITE: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding; Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal